Since January 1, 2023, the Agec law (anti-waste for a circular economy) requires marketers to communicate on each product a list of essential information to inform their purchasing decisions “product sheet relating to environmental qualities and characteristics »: the traceability of the production chain, the dangerousness of the substances present and the risks of plastic microfibers linked to the use of synthetic materials. The law also requires notification of the presence of recycled materials as well as the recyclability of each product.
Origin, health risks, environmental impact... Transparency is now displayed directly in stores to respond to the main concerns of increasingly demanding consumers. For brands, producers and importers, the pressure is increasing because the AGEC law foreshadows the arrival of another regulation in 2024: environmental labeling .

The challenge is significant but the solutions exist, digital and adapted to the size of each operator to activate passports produced on each label. This is what reveals the state of the art of the Transparency and Traceability working group of the BALI Chair presented to industry professionals during the last edition of Biarritz Good Fashion and accessible to all from the Chair website BALI.
Produced by Pantxika Ospital , PhD student in charge of the thesis “Transparency and Traceability” carried by Belharra Numérique , with the contribution of Bixente Demarcq , study engineer at ESTIA , and the support of Paris Good Fashion , the deliverable lists and analyzes for the first time the concepts, solutions and best practices
in Europe.
Objective: to enable marketers to see more clearly in order to choose the right tools.

We have produced a white paper on the theme of traceability based on the results of this study and our feedback as publisher of the e-SCM solution, dedicated to managing the supply process for brands in the fashion & luxury. You can download it below depending on your choice of language:
The product passport makes the link between traceability and transparency . This passport allows the information presented on the product label dynamically. It provides access to information on the origin, composition, repair and dismantling possibilities, as well as the treatment of products at the end of their life. This information helps promote circularity by facilitating maintenance, repair, resale, rental, dismantling and recycling.
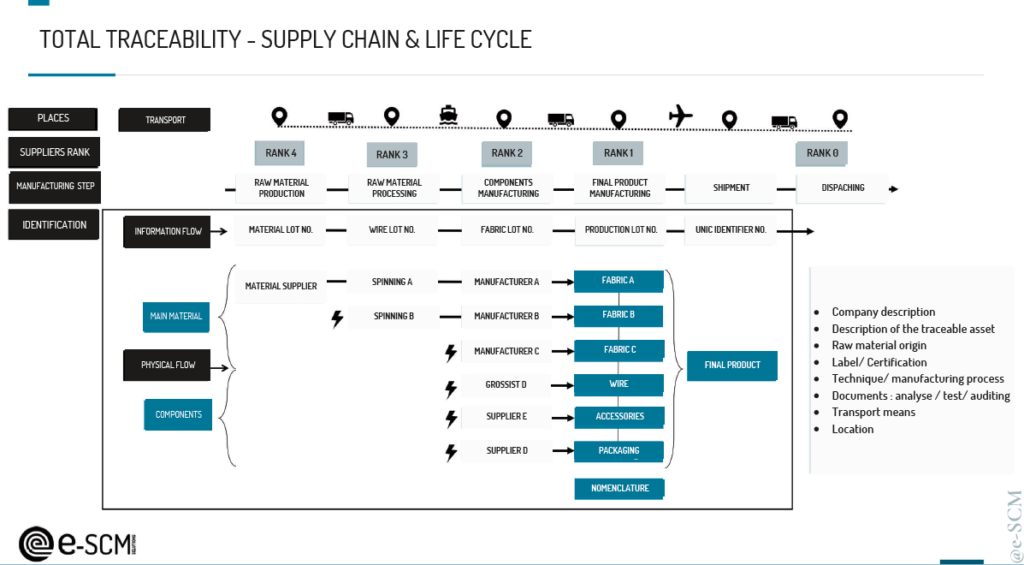
Understand the challenges for the fashion sector
For products in the fashion and textile , transparency can be defined as accessibility to traceability information. In a globalized context in which brands outsource their production, traceability can allow them to better understand their supply chain to comply with the duty of vigilance and thus collect all the elements for a reliable audit trail.
This data collection is the main issue of traceability, the transparency of fashion companies relies on the reliability of this information. In return, this information could promote:
Technological means supporting traceability
There are several types of digital traceability solutions:
Technological means supporting transparency
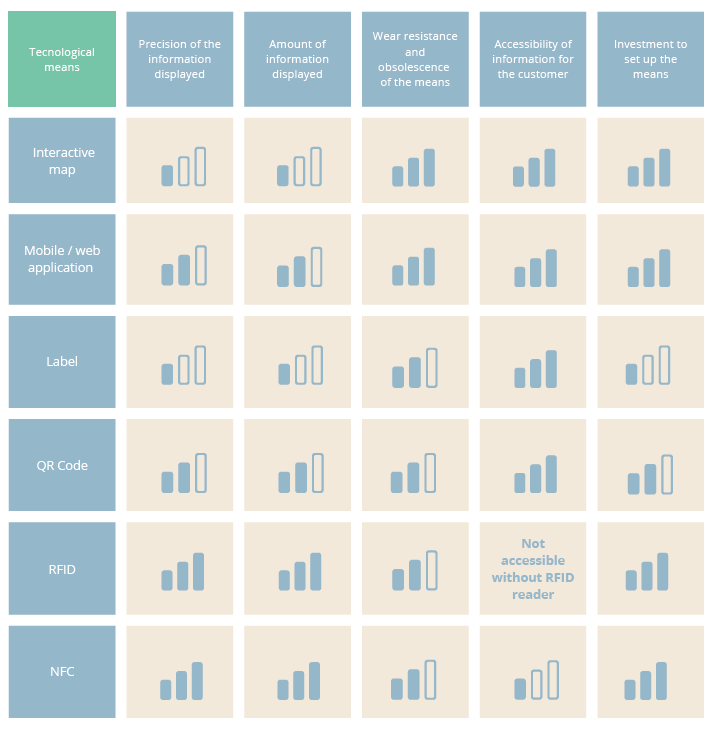
Source: Report “State of the art of traceability and transparency solutions”, traceability working group, BALI Chair | Paris Good Fashion | Belharra Digital
